Chemical Material Anesthetics auxiliary drugs CAS 59-46-1 PROCAINE
Wickr/Telegram : Daisey521
Whatsapp : 008618034511316
Skype: live:.cid.93f1bd48473d87a8
Email: saleroom@yeah.net
Basic Information
Description
Procaine is a local anesthetic with a para-amino function. Sensitization mainly concerns medical, dental and veterinary professions.
Chemical Properties
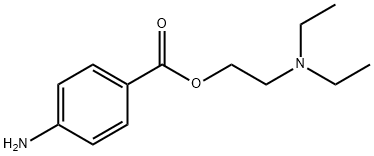
The hydrochloride salt of 2-(diethylamino) ethyl p-aminobenzoate (C13H21ClN2O2 or N2C6H4COOCH2CH2NH(C2H5)2HCl) is generally referred to as procaine. Although the PABA ester is insoluble in water, the hydrochloride salt is very soluble in water.
Uses
1.Procaine (Novocain) is mainly used in dental or medical procedures requiring infiltration anesthesia, peripheral block, or spinal block.
2.inhibitor of sodium channel
3. Procaine is a sodium channel blocker and inhibitor of a variety of processes.



Usage
Clinical Use Procaine is very quickly metabolizedin the plasma by cholinesterases and in the liver via ester hydrolysisby a pseudocholinesterase. The in vitroelimination half-life is approximately 60 seconds. Any conditionthat decreases the cholinesterase concentration may increaseexposure to procaine and potential toxicity. Decreasedenzyme activity can be found with genetic deficiency, liverdisease, malignancy, malnutrition, renal failure, burns, thirdtrimester of pregnancy, and following cardiopulmonary bypasssurgery. Ester hydrolysis produces PABA, the compoundresponsible for the allergic reactions common to theester anesthetics. Procaine is not used topically because of itsinability to pass through lipid membranes and finds use as aninfiltration agent for cutaneous or mucous membranes, forshort procedures. Procaine is also used for peripheral nerveblock and as an epidural agent to diagnose pain syndromes.